Written by Anjani Mishra
Brain
The
brain is the enlarged rostral part of the central nervous system (CNS) and is
situated in the cranial cavity.
For instructive purposes and for the convenient description of the gross anatomical relations, the brain can be divided into;
i.
Cerebrum,
ii.
Cerebellum,
&
iii.
Brain
stem.
i. Cerebrum: the cerebrum, which is the largest part of the brain, is separated from the caudally located cerebellum by a deep fissure and subdivided into two symmetrical halves, the hemisphere by a longitudinal fissure. The hemispheres have numerous depressions and convolutions on their surfaces known as sulcus and gyrus.
ii. Cerebellum: the cerebellum is situated caudal to the cerebrum and dorsal to the brain stem (medulla oblongata)
iii. Brain stem: brain stem is situated on the basal side of the brain and is covered by the other two parts, i.e. cerebrum and cerebellum. From its caudal end (medulla oblongata), continuation of spinal cord begins that ends about mid sacrum as a caudal limit in domestic animals. It consists of cerebral peduncle/crura rostrally, pons centrally and medulla oblongata caudally.
Derivatives of principal parts of brain
|
Initial segments |
Primary segments |
Secondary segments |
Principal derivatives |
cavities |
|
Procencephalon
|
Procencephalon (rostral
vesicle) |
Telencephalon
(proximal
part) |
Cerebral
hemisphere, optic chaisma, olfactory bulb |
Lateral
ventricle |
|
|
|
Diencephalon (distal
part) |
Epithalamus,
thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal body |
Third
ventricle |
|
Rhombencephalon
|
Mesencephalon
(middle
vesicle) |
Mesencephalon (proximal
& middle) |
Cerebral
crura, Corpora
quadrigemina |
Mesencephalic
equeduct or cerebral equeduct |
|
|
Rhombencephalon (caudal
vesicle) |
Metencephalon
(proximal
& rostral) |
Pons,
cerebellum |
Fourth
ventricle |
|
|
|
Myelencephalon
(distal
and caudal) |
Medulla
oblongata |
Fourth ventricle |
Ventricles
of the brain
The internal brain cavities are referred to as
ventricles and caudally are continuous with the central canal of the spinal
cord.
The fourth ventricle is situated between the
cerebellum and the medulla oblongata; the third ventricle is situated in the
diencephalon (around the thalamus) and surrounds the interthalamic adhesion,
and the two lateral ventricles (first and second ventricles) are found within
the two cerebral hemispheres.
The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid and
communicates through the two lateral apertures of the fourth ventricles
(foramina of Luschka) with the subarachnoid cavity. The median aperture
(foramen of Megendie) and the aperture of the terminal ventricle of the spinal
cord are of questionable existence in the common domestic animals.
Cranial
Nerves:
Type and distribution:
|
S.No. |
Name |
Type |
Distribution |
|
(i) |
Olfactory
(SVA) |
Sensory |
Nasal
mucous membrane (sense of smell) |
|
(ii) |
Optic
(SSA) |
Sensory |
Retina
of eye (sense of sight) |
|
(iii) |
Oculomotor
(GSE) |
Motor |
Most
of the muscles of eye |
|
(iv) |
Trochlear
(GSE) (smallest) |
Motor |
Dorsal
oblique muscle of the eye |
|
(v) |
Trigeminal
(GSA, (largest) SVE) |
Mixed |
Sensory-
to eye and face Motor-
to the muscles of mastication |
|
(vi) |
Abducent
(GSE, GSA) |
Motor |
Retractor
and lateral rectus muscle of the eye |
|
(vii) |
Facial
(GSA, GVE, GVA, SVE, SVA) |
Mixed |
Sensory-
ear and taste to rostral 2/3 of the tongue Motor-
muscles of facial expression |
|
(viii) |
Acoustic
or vestibule-cochlear (SSA) |
sensory |
Cochlea(hearing)
and semicircular canal(equilibrium) |
|
(ix) |
Glossopharyngeal (GSA,
GVE, GVA, SVE, SVA) |
Mixed |
Sensory-
to pharynx and taste to caudal 1/3 of the tongue Motor-
to the muscles of pharynx |
|
(x) |
Vagus
(longest & widely distributed) (GSA,
GVE, GVA, SVE, SVA) |
Mixed |
Sensory-
to pharynx and larynx Motor-
to the muscles of larynx |
|
(xi) |
Spinal
accessory (SVE, GSA) |
Motor |
To
the muscles of the shoulder and neck |
|
(xii) |
Hypoglossal
(GSE, GSA) |
Motor |
To
the muscles of the tongue |
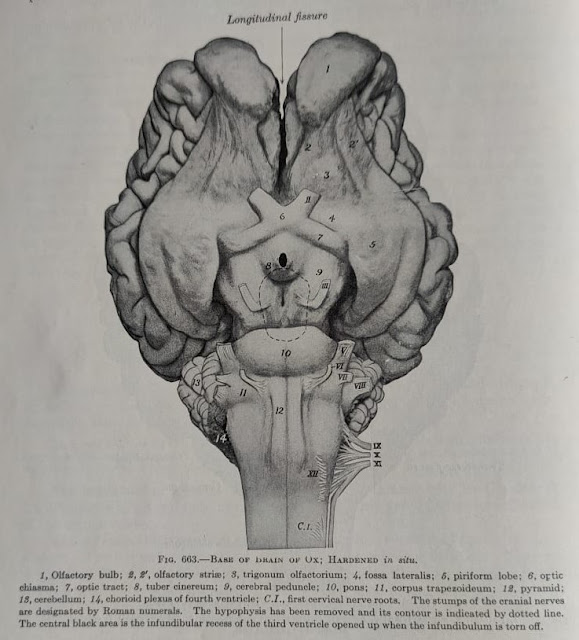
Most of the cranial nerves emerge from the basal surface of the brain
- The first olfactory nerve emerges with numerous small fibers from the convex surface of the olfactory bulb.
- The second optic nerve appears on the ventral surface between the piriform lobes and the cerebral crura/peduncle.
- The third oculomotor nerve arises from the intercrural fossa(interpeduncular fossa).
- The fourth trochlear nerve emerges between the pons and cerebrum.
- The fifth trigeminal nerve arises from the lateral part of the pons and is comprised of two roots, a sensory roots and a motor root.
- The sixth abducent nerve emerges between the lateral edge of the pyramid and the caudal edge of trapezoid body(corpus trapezoideum).
- The seventh facial nerve originates between the sixth(abducent) nerve and eighth(vestibulo-cochlear) nerve, caudo-lateral to the pons on the trapezoid body.
- The eighth vestibulo-cochlear originates a few millimeter caudo-lateral to the seventh (facial) nerve at the lateral extremity of the trapezoid body.
- The ninth glossopharyngeal, the tenth vagus and the eleventh spinal accessory nerves are connected by a linear series of roots with the lateral aspect of the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata.
- The twelfth hypoglossal nerve arises from the ventral lateral sulcus in a line along the lateral edge of the pyramids in the caudal portion of the medulla oblongata.
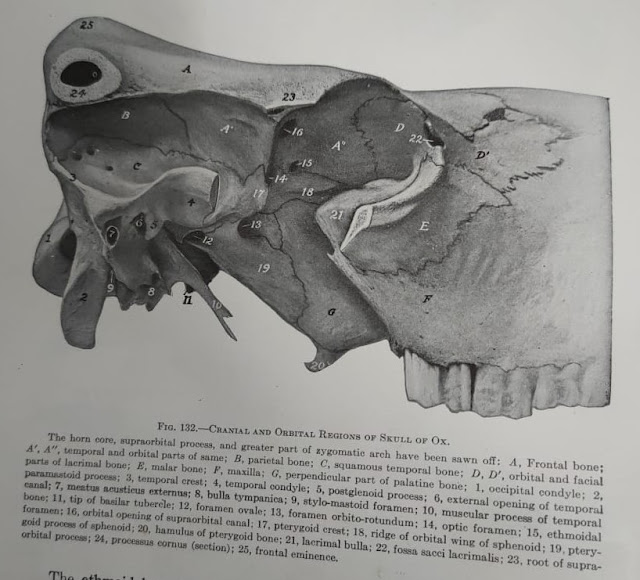
Foramina of the skull
|
S.No. |
Name of the
foramina |
Structures |
|
1 |
Foramem
magnum |
Medulla
oblongata, spinal cord with its covering |
|
2 |
Condyloid
foramen |
Condyloid
artery and vein |
|
3 |
Foramen
lacerum or jugular foramen in ruminant |
Vagus
nerve, internal carotid artery, glossopharyngeal nerve, spinal accessory and
ventral cerebral vein |
|
4 |
Stylomastoid
|
Facial
nerve |
|
5 |
Mastoid |
Caudal
meningeal artery & vein |
|
6 |
Foramen
ovale |
Mandibular
nerve |
|
7 |
Foramen
orbito-rotundum |
Trigeminal(ophthalmic,
maxillary), oculomotor, and abducent nerve |
|
8 |
Optic
foramen |
Optic
nerve |
|
9 |
Ethmoid
foramen |
Ethmoid
vessels and nerves |
|
10 |
Supraorbital
foramen |
Supra-orbital
artery and vein |
|
11 |
Infra-orbital
foramen |
Infra-orbital
artery and vein |
|
12 |
Mandibular
foramen |
Mandibular
vessels and nerves |
|
13 |
Mental
foramen |
Mental
artery, vein and nerve |
|
14 |
Anterior
palatine |
Palatine
artery, vein and nerve |
|
15 |
Posterior
palatine |
Palatine
artery |
|
16 |
Sphenopalatine |
Sphenopalatine
nerve, posterior nasal artery and vein |
|
17 |
The
cribriform foramina |
Approx.
300 in number in dog. They transmit olfactory nerve filament from the nasal
mucosa to the olfactory bulb of the brain |
Facebook Veterinary group










Post a Comment